- What is a DuMuX model
- What is a DuMuX model
- What is a DuMuX model
- What is a DuMuX model
- LocalResidual
- LocalResidual
- Example: Diffusion equation
- Example: Diffusion equation
- Example: Diffusion equation
- LocalResidual
- Storage term
- Flux term
- Flux term
- Flux term
- Flux term
- LocalResidual
- Model properties
- Model type tag
- Model properties
- Defining model properties
- Defining model properties
- Defining model properties
- Exercise: Model
- Exercise: Model
- Tasks
title: Implementing a Model in DuMuXWhat is a DuMuX model
What is a DuMuX model
A DuMuX model is an implementation of a discretized mathematical model, generally given by partial differential equations.
What is a DuMuX model
Mathematical model (PDE):

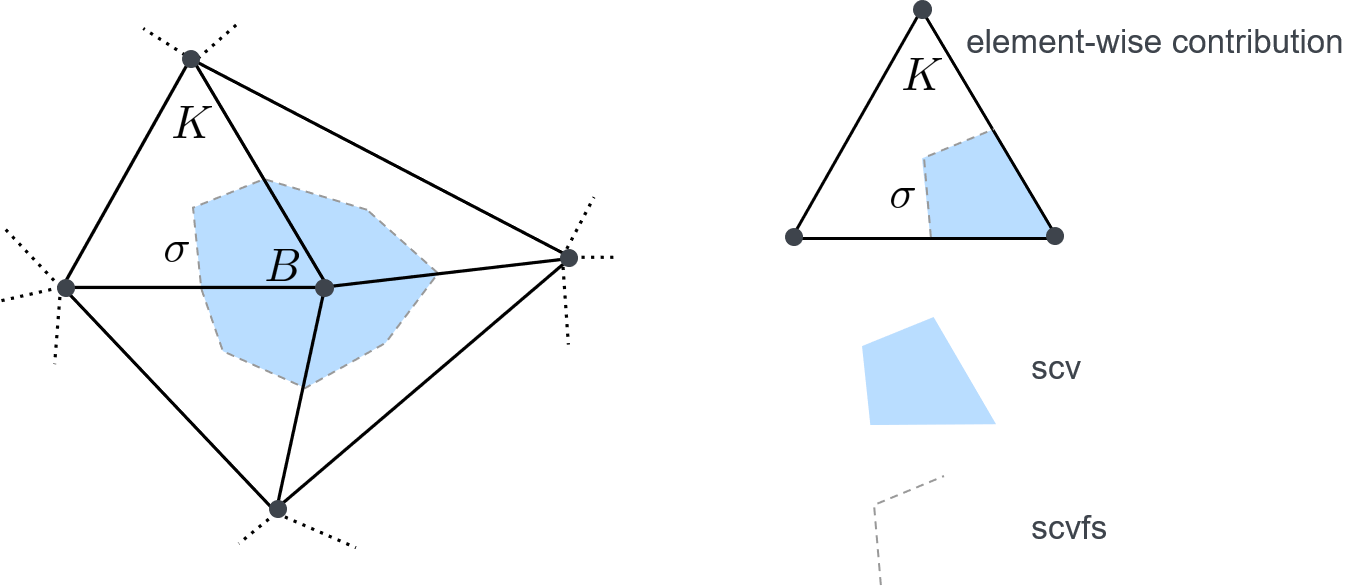
Discrete model, e.g. using finite volumes:
What is a DuMuX model
Discrete model, e.g. using finite volumes:
-
: storage term
-
: flux term over sub control volume face (scvf)
-
source term
Where to implement these terms in DuMuX?
LocalResidual
LocalResidual
LocalResidual
Implements terms of a PDE in the functions
computeStorage(...)computeFlux(...)computeSource(...)
Example: Diffusion equation
Mathematical model (PDE):
with
-
: concentration
-
: constant diffusion coefficient
-
: spatial domain
-
: end time
Example: Diffusion equation
Discrete model using the Box discretization:
with
-
: concentration at timeand control volume
-
c^n_h: global discrete solution at timet_n, interpolated using basis functions
-
\mathbf{n}: unit outer normal vector
-
\sigma: sub control volume face (scvf)
Example: Diffusion equation
Discrete model using the Box discretization:
LocalResidual
The local residual of the diffusion model:
template<class TypeTag>
class DiffusionModelLocalResidual
: public GetPropType<TypeTag, Properties::BaseLocalResidual>
{
...
}Inherits from the BaseLocalResidual, which is chosen depending on the discretization scheme, here Box scheme.
Storage term
NumEqVector computeStorage(const Problem& problem,
const SubControlVolume& scv,
const VolumeVariables& volVars) const
{
NumEqVector storage;
storage[Indices::massBalanceEqIdx]
= volVars.priVar(Indices::concentrationIdx);
return storage;
}Flux term
with
-
c^n_h: global discrete solution at timet_n, interpolated using basis functions
-
\mathbf{n}: unit outer normal vector
-
\sigma: sub control volume face (scvf)
Flux term
NumEqVector computeFlux(const Problem& problem,
const Element& element,
const FVElementGeometry& fvGeometry,
const ElementVolumeVariables& elemVolVars,
const SubControlVolumeFace& scvf,
const ElementFluxVariablesCache& elemFluxVarsCache) const
{
...
}Flux term
NumEqVector computeFlux(...) const
{
// Compute ∇c
const auto& fluxVarCache = elemFluxVarsCache[scvf];
Dune::FieldVector<Scalar, dimWorld> gradConcentration(0.0);
for (const auto& scv : scvs(fvGeometry))
{
const auto& volVars = elemVolVars[scv];
gradConcentration.axpy(
volVars.priVar(Indices::concentrationIdx),
fluxVarCache.gradN(scv.indexInElement())
);
}
...
}Flux term
NumEqVector computeFlux(...) const
{
...
NumEqVector flux;
// Compute the flux
flux[Indices::massBalanceEqIdx] = -1.0*scvf.area()*vtmv(
scvf.unitOuterNormal(),
problem.diffusionCoefficient(),
gradConcentration
);
return flux;
}
LocalResidual
A LocalResidual implements the discretized mathematical model.
For its implementation different model-specific properties have to be set
Model properties
Model type tag
The property tag is an empty struct with the respective name, e.g. DiffusionModel
namespace Dumux::Properties::TTag {
//! The diffusion model tag that we can specialize properties for
struct DiffusionModel {};
} // end namespace Dumux::Properties::TTagModel properties
We can set nodel properties for the DiffusionModel type tag
All properties are defined within the namespace Dumux::Properties
namespace Dumux::Properties {
//define all properties
} // end namespace Dumux::PropertiesDefining model properties
The type of the local residual is the class DiffusionModelLocalResidual defined from earlier
template<class TypeTag>
struct LocalResidual<TypeTag, TTag::DiffusionModel>
{ using type = DiffusionModelLocalResidual<TypeTag>; };Defining model properties
The model traits specify information about the model:
template<class TypeTag>
struct ModelTraits<TypeTag, TTag::DiffusionModel>
{
struct type
{
struct Indices
{
static constexpr int concentrationIdx = 0;
static constexpr int massBalanceEqIdx = 0;
};
static constexpr int numEq() { return 1; }
};
};Defining model properties
Further model specific properties can be set accordingly by using the model property tag,
i.e. TTag::DiffusionModel
Exercise: Model
Exercise: Model
Implementation of a nonlinear diffusion model for denoising of an MRI image

Tasks
- Implement local residual
- Set model properties
- Use model in test case
- Customize volume variables